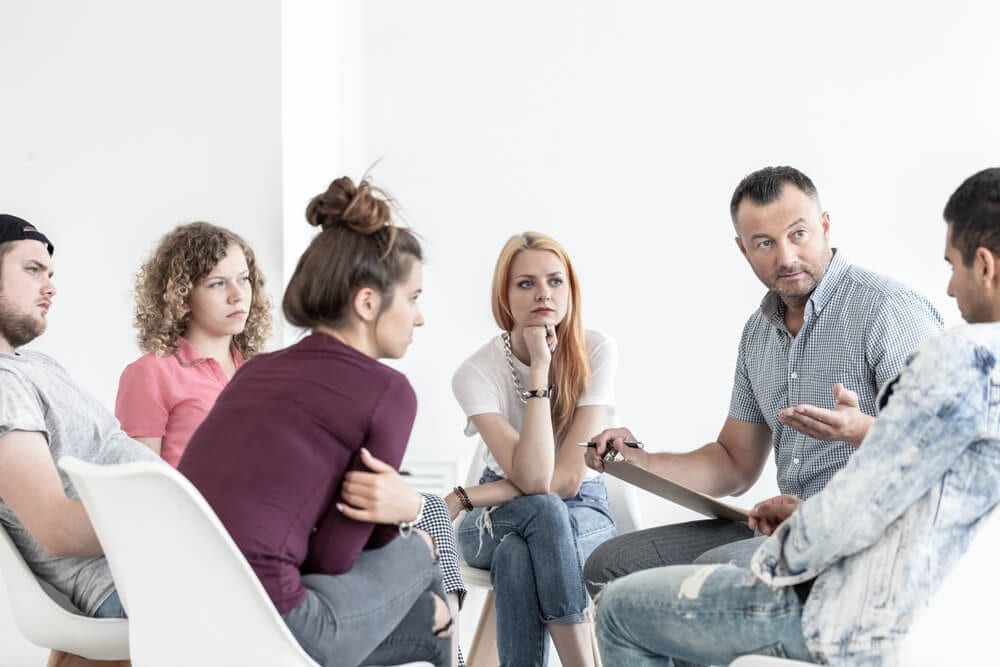
The majority of drugs have an effect on the "reward circuit" in the brain, which causes pleasure and also floodings the mind with the chemical carrier dopamine. A well functioning reward system boosts a person to repeat activities needed to prosper, such as eating and also hanging around with liked ones. The surges of dopamine that happen in the reward circuit are what cause the reinforcement of behaviors that are pleasurable but unsafe, like as substance abuse. This consequently creates people to participate in the activity once again.
When an individual remains to take medications, their mind will certainly change by lowering the capability of cells in the incentive circuit to react to it. This will occur as long as the individual continues to make use of medicines. This sensation, referred to as resistance, has the result of decreasing the high that the specific experiences in contrast to the high that they had when they originally took the medication. They can attempt to achieve the very same high by consuming a higher amount of the compound. As a result of these mind adjustments, the private often finds that they are not able to get pleasure from other points that they used to enjoy, such as eating, sex, or social tasks.
Lasting use also generates changes in other chemical systems as well as circuits in the mind, which can have an effect on a variety of cognitive as well as behavioural procedures, such as discovering, judgement, decision-making, anxiety, memory, and also behavior. Because of the nature of dependency, lots of people that utilize medications remain to do so despite the fact that they recognize the potentially negative consequences of their practices.